The legend is that Newton discovered the important law of physics
Force = Mass * Acceleration
when he was struck by an apple falling from an apple tree. By studying the motion of the apple, Newton determined its acceleration. By knowing the mass of the apple and its acceleration, Newton could determine the resultant verical force on the apple.
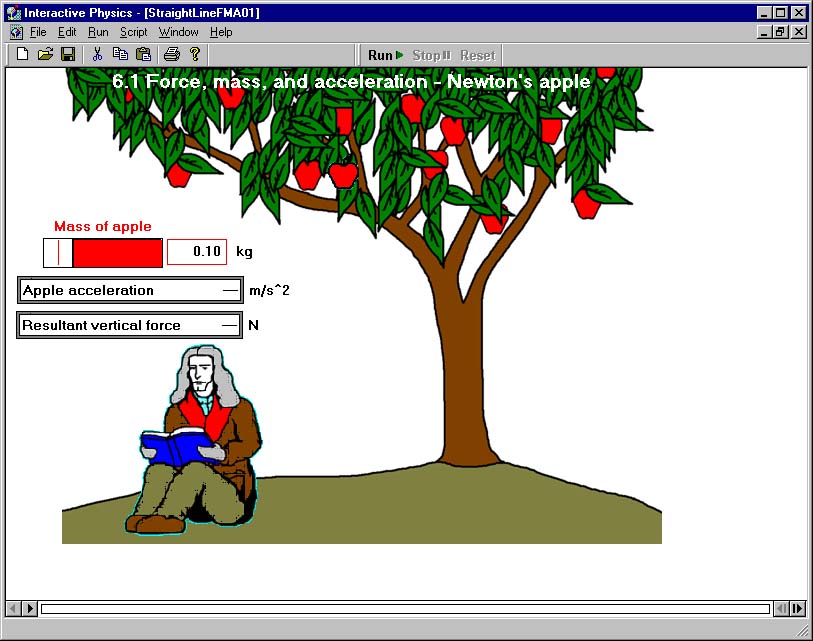
- Using time-motion studies, the acceleration of a 0.1-kg apple is determined to be
9.8 m/sec2. What is the resultant vertical force on the apple?
Result:0.1 kg * 9.8 m/sec2 = 0.98 newtons
- A 0.2-kg apple falls with an acceleration of 9.8 m/sec2.
What is the resultant vertical force on the apple?
Result:0.2 kg * 9.8 m/sec2 = 1.96 newtons
- What is the resultant vertical force on a 0.3-kg apple that falls with an
acceleration of 9.8 m/sec2?
Result:0.3 kg * 9.8 m/sec2 = 2.94 newtons
- What is the resultant vertical force on a 0.4-kg apple that falls with an
acceleration of 9.8 m/sec2?
Result:0.4 kg * 9.8 m/sec2 = 3.92 newtons
- Bonus question - answer without Interactive Physics.
The downward gravitational force on any object near Earth is equal to the object's mass multiplied by Earth's gravitational constant, 9.8 m/sec2, i.e.,ForceFromGravity = Mass * Gravity
What is the gravitational force on a woman whose mass is 50 kg?
Result:50 kg * 9.8 m/sec2 = 490 newtons
Copyright © 2006-09 by Design Simulation Technologies, Inc.